Nomenclature |
|---|
The
increasingly large number of organic compounds identified with each
passing day, together with the fact that many of these compounds are
isomers of other compounds, requires that a systematic nomenclature
system be developed. Just as each distinct compound has a unique
molecular structure which can be designated by a structural formula,
each compound must be given a characteristic and unique name.
As
organic chemistry grew and developed, many compounds were given
trivial names, which are now commonly used and recognized. Some
examples are:
| Name | Methane | Butane | Acetone | Toluene | Acetylene | Ethyl Alcohol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formula | CH4 | C4H10 | CH3COCH2 | CH3C6H5 | C2H2 | C2H5OH |
Such common names often have their origin in the history of the science and the natural sources of specific compounds, but the relationship of these names to each other is arbitrary, and no rational or systematic principles underly their assignments.
A rational
nomenclature system should do at least two things. First, it should
indicate how the carbon atoms of a given compound are bonded
together in a characteristic lattice of chains and rings. Second, it
should identify and locate any functional groups present in the
compound. Since hydrogen is such a common component of organic
compounds, its amount and locations can be assumed from the
tetravalency of carbon, and need not be specified in most cases.
The IUPAC nomenclature system is a set of logical rules devised
and used by organic chemists to circumvent problems caused by
arbitrary nomenclature. Knowing these rules and given a structural
formula, one should be able to write a unique name for every
distinct compound. Likewise, given a IUPAC name, one should be able
to write a structural formula. In general, an IUPAC name will have
three essential features:
• A root or base indicating a major chain
or ring of carbon atoms found in the molecular
structure.
• A suffix or other element(s)
designating functional groups that may be present in the
compound.
• Names of substituent groups, other than
hydrogen, that complete the molecular
structure.
As an introduction to the IUPAC nomenclature system, we shall first consider compounds that have no specific functional groups. Such compounds are composed only of carbon and hydrogen atoms bonded together by sigma bonds (all carbons are sp3 hybridized).
Alkanes |
|---|
Hydrocarbons having no double or triple bond
functional groups are classified as alkanes or
cycloalkanes, depending on whether the carbon atoms of the
molecule are arranged only in chains or also in rings. Although
these hydrocarbons have no functional groups, they constitute the
framework on which functional groups are located in other classes of
compounds, and provide an ideal starting point for studying and
naming organic compounds. The alkanes and cycloalkanes are also
members of a larger class of compounds referred to as
aliphatic. Simply put, aliphatic compounds are compounds that
do not incorporate any aromatic rings in their molecular
structure.
The following table lists the IUPAC names assigned to
simple continuous-chain alkanes from C-1 to C-10. A common
"ane" suffix identifies these compounds as alkanes. Longer
chain alkanes are well known, and their names may be found in many
reference and text books. The names methane through
decane should be memorized, since they constitute the root of
many IUPAC names. Fortunately, common numerical prefixes are used in
naming chains of five or more carbon atoms.
| Name | Molecular Formula |
Structural Formula |
Isomers | Name | Molecular Formula |
Structural Formula |
Isomers | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| methane | CH4 | CH4 | 1 | hexane | C6H14 | CH3(CH2)4CH3 | 5 | |
| ethane | C2H6 | CH3CH3 | 1 | heptane | C7H16 | CH3(CH2)5CH3 | 9 | |
| propane | C3H8 | CH3CH2CH3 | 1 | octane | C8H18 | CH3(CH2)6CH3 | 18 | |
| butane | C4H10 | CH3CH2CH2CH3 | 2 | nonane | C9H20 | CH3(CH2)7CH3 | 35 | |
| pentane | C5H12 | CH3(CH2)3CH3 | 3 | decane | C10H22 | CH3(CH2)8CH3 | 75 |
Some important behavior trends and terminologies:
(i) The formulas and structures of these alkanes
increase uniformally by a CH2
increment.
(ii) A uniform variation of this
kind in a series of compounds is called homologous.
(iii) These formulas all fit the CnH2n+2 rule.
This is also the highest possible H/C ratio for a stable
hydrocarbon.
(iv) Since the H/C ratio in these
compounds is at a maximum, we call them saturated (with
hydrogen).
Beginning with butane (C4H10), and becoming more numerous with larger alkanes, we note the existence of alkane isomers. For example, there are five C6H14 isomers, shown below as abbreviated line formulas (A through E):
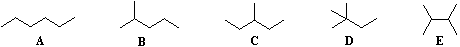
Although these distinct compounds all have the same molecular formula, only one (A) can be called hexane. How then are we to name the others?
The IUPAC system requires first that we have names for simple unbranched chains, as noted above, and second that we have names for simple alkyl groups that may be attached to the chains. Examples of some common alkyl groups are given in the following table. Note that the "ane" suffix is replaced by "yl" in naming groups. The symbol R is used to designate a generic (unspecified) alkyl group.
| Group | CH3– | C2H5– | CH3CH2CH2– | (CH3)2CH– | CH3CH2CH2CH2– | (CH3)2CHCH2– | CH3CH2CH(CH3)– | (CH3)3C– | R– |
| Name | Methyl | Ethyl | Propyl | Isopropyl | Butyl | Isobutyl | sec-Butyl | tert-Butyl | Alkyl |
IUPAC Rules for Alkane Nomenclature 1. Find and name the longest continuous
carbon chain. |
For the above isomers of hexane the IUPAC names are: B 2-methylpentane C 3-methylpentane D 2,2-dimethylbutane E 2,3-dimethylbutane
Halogen substituents are easily accomodated, using the names: fluoro (F-), chloro (Cl-), bromo (Br-) and iodo (I-). For example, (CH3)2CHCH2CH2Br would be named 1-bromo-3-methylbutane. If the halogen is bonded to a simple alkyl group an alternative "alkyl halide" name may be used. Thus, C2H5Cl may be named chloroethane (no locator number is needed for a two carbon chain) or ethyl chloride.
Cycloalkanes |
|---|
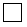
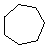
Cycloalkanes have one or more rings of carbon atoms. The simplest examples of this class consist of a single, unsubstituted carbon ring, and these form a homologous series similar to the unbranched alkanes. The IUPAC names of the first five members of this series are given in the following table. The last (yellow shaded) column gives the general formula for a cycloalkane of any size. If a simple unbranched alkane is converted to a cycloalkane two hydrogen atoms, one from each end of the chain, must be lost. Hence the general formula for a cycloalkane composed of n carbons is CnH2n.
| Name | Cyclopropane | Cyclobutane | Cyclopentane | Cyclohexane | Cycloheptane | Cycloalkane |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Formula |
C3H6 | C4H8 | C5H10 | C6H12 | C7H14 | CnH2n |
| Structural Formula |
 |
 |
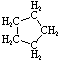 |
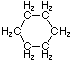 |
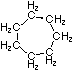 |
(CH2)n |
| Line Formula |
 |
 |
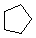 |
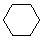 |
 |
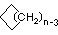 |
Substituted cycloalkanes are named in a fashion very similar to that used for naming branched alkanes. The chief difference in the rules and procedures occurs in the numbering system. Since all the carbons of a ring are equivalent (a ring has no ends like a chain does), the numbering starts at a substituted ring atom.
IUPAC Rules for Cycloalkane Nomenclature 1. For a monosubstituted cycloalkane
the ring supplies the root name (table above) and the
substituent group is named as usual. A location number is
unnecessary. |
Small rings, such as three and four membered rings, have significant angle strain resulting from the distortion of the sp3 carbon bond angles from the ideal 109.5º to 60º and 90º respectively. This angle strain often enhances the chemical reactivity of such compounds, leading to ring cleavage products. It is also important to recognize that, with the exception of cyclopropane, cycloalkyl rings are not planar (flat). The three dimensional shapes assumed by the common rings (especially cyclohexane and larger rings) are described and discussed in the Conformational Analysis Section.
Hydrocarbons having more than one ring are common, and are referred to as bicyclic (two rings), tricyclic (three rings) and in general, polycyclic compounds. The molecular formulas of such compounds have H/C ratios that decrease with the number of rings. In general, for a hydrocarbon composed of n carbon atoms associated with m rings the formula is: CnH(2n + 2 - 2m). The structural relationship of rings in a polycyclic compound can vary. They may be separate and independent, or they may share one or two common atoms. Some examples of these possible arrangements are shown in the following table.
| Isolated Rings | Spiro Rings | Fused Rings | Bridged Rings |
|---|---|---|---|
| No common atoms | One common atom | One common bond | Two common atoms |
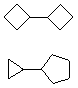 |
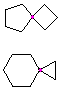 |
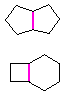 |
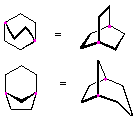 |
Alkenes & Alkynes |
|---|
Alkenes and alkynes are hydrocarbons which respectively have carbon-carbon double bond and carbon-carbon triple bond functional groups. The molecular formulas of these unsaturated hydrocarbons reflect the multiple bonding of the functional groups:
| Alkane | R–CH2–CH2–R | CnH2n+2 | This is the maximum H/C ratio for a given number of carbon atoms. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alkene | R–CH=CH–R | CnH2n | Each double bond reduces the number of hydrogen atoms by 2. |
| Alkyne | R–C≡C–R | CnH2n-2 | Each triple bond reduces the number of hydrogen atoms by 4. |
As noted earlier in the Analysis of Molecular Formulas section, the molecular formula of a hydrocarbon provides information about the possible structural types it may represent. For example, consider compounds having the formula C5H8. The formula of the five-carbon alkane pentane is C5H12 so the difference in hydrogen content is 4. This difference suggests such compounds may have a triple bond, two double bonds, a ring plus a double bond, or two rings. Some examples are shown here, and there are at least fourteen others!
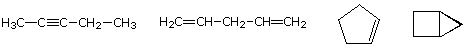
IUPAC Rules for Alkene and Cycloalkene Nomenclature 1. The ene suffix
(ending) indicates an alkene or
cycloalkene. |
IUPAC Rules for Alkyne Nomenclature 1. The yne suffix
(ending) indicates an alkyne or
cycloalkyne. |
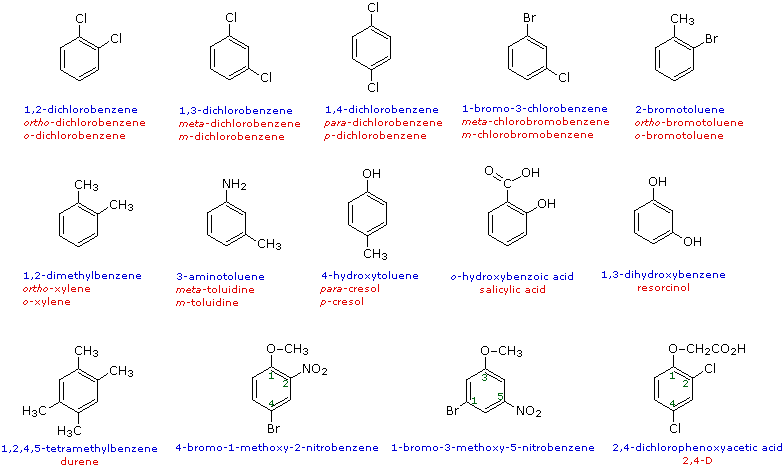
Benzene Derivatives |
|---|
The nomenclature of substituted benzene ring compounds is less systematic than that of the alkanes, alkenes and alkynes. A few mono-substituted compounds are named by using a group name as a prefix to "benzene", as shown by the combined names listed below. A majority of these compounds, however, are referred to by singular names that are unique. There is no simple alternative to memorization in mastering these names.
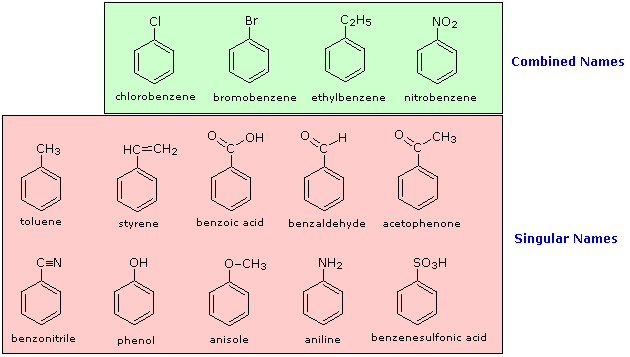
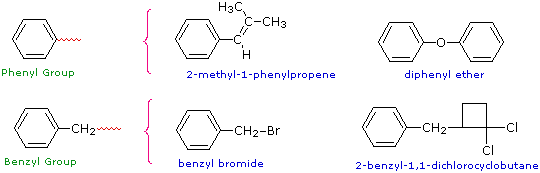
Two commonly encountered substituent groups that incorporate a benzene ring are phenyl, abbreviated Ph-, and benzyl, abbreviated Bn-. These are shown here with examples of their use. Be careful not to confuse a phenyl (pronounced fenyl) group with the compound phenol (pronounced feenol). A general and useful generic notation that complements the use of R- for an alkyl group is Ar- for an aryl group (any aromatic ring).
When more than one substituent is present on a benzene ring, the relative locations of the substituents must be designated by numbering the ring carbons or by some other notation. In the case of disubstituted benzenes, the prefixes ortho, meta & para are commonly used to indicate a 1,2- or 1,3- or 1,4- relationship respectively. In the following examples, the first row of compounds show this usage in red. Some disubstituted toluenes have singular names (e.g. xylene, cresol & toluidine) and their isomers are normally designated by the ortho, meta or para prefix. A few disubstituted benzenes have singular names given to specific isomers (e.g. salicylic acid & resorcinol). Finally, if there are three or more substituent groups, the ring is numbered in such a way as to assign the substituents the lowest possible numbers, as illustrated by the last row of examples. The substituents are listed alphabetically in the final name. If the substitution is symmetrical (third example from the left) the numbering corresponds to the alphabetical order.